As energy costs continue to rise and environmental concerns become increasingly urgent, homeowners around the world are turning their attention skyward, toward the sun. Solar panels have transformed from a niche technology into a mainstream energy solution, adorning rooftops across neighbourhoods and promising both financial savings and environmental benefits. But what exactly are solar panels, and are they truly worth the investment? This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about solar energy and how to bring it to your home.
What Is a Solar Panel?
The Basic Definition
A solar panel, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) panel, is a device that converts sunlight into electricity through a fascinating scientific process. At its core, a solar panel consists of numerous solar cells made primarily from silicon, a semiconductor material that exhibits unique electrical properties when exposed to light.
How Solar Panels Work: The Science Behind the Power
The magic happens at the molecular level. Each solar cell contains two layers of silicon that have been specially treated, one with phosphorus to create a negative charge, and another with boron to create a positive charge. When sunlight strikes these cells, photons from the light knock electrons loose from the silicon atoms. This creates an electrical field between the two layers, causing the electrons to flow in a specific direction, generating direct current (DC) electricity.
The Physical Structure of Solar Panels
Modern solar panels typically contain 60 to 72 individual cells, all working together to produce usable electricity. These cells are protected by a durable glass covering on the front and a backing material on the rear, with an aluminium frame holding everything together. The entire assembly is designed to withstand decades of exposure to rain, wind, hail, and temperature fluctuations.
Power Output and Efficiency
Most residential solar panels today produce between 250 and 400 watts of power under ideal conditions. The efficiency of these panels, meaning how much sunlight they can convert into electricity, ranges from 15% to 22% for commercially available models, with premium panels achieving even higher efficiency rates.
Complete Solar System Components
It’s important to understand that solar panels produce DC electricity, but homes run on alternating current (AC) electricity. This is where an inverter comes into play, converting the DC power from your panels into AC power that your appliances can use. Additionally, a complete solar system includes mounting hardware, wiring, a monitoring system to track performance, and often a battery storage system for excess energy.

Is Solar Really a Good Investment?
The question of whether solar panels represent a worthwhile investment doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all answer, but for many homeowners, the financial case is compelling. Let’s examine the key factors that determine solar’s value proposition.
Financial Returns and Payback Period
The primary financial benefit of solar panels is the reduction or elimination of your monthly electricity bill. Depending on your location, energy consumption, and system size, most homeowners see payback periods ranging from 6 to 12 years. After this point, you’re essentially generating free electricity for the remaining life of your system, which typically extends 25 to 30 years or more.
Consider a household paying $150 monthly for electricity. Over 25 years, that amounts to $45,000 in utility costs (without accounting for rate increases, which average 2-3% annually). A solar system might cost $15,000 to $25,000 after incentives, representing substantial long-term savings.
Incentives and Tax Benefits
Government incentives dramatically improve solar’s financial appeal. In the United States, the federal solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) currently allows homeowners to deduct 30% of installation costs from their federal taxes. Many states and local utilities offer additional rebates, performance payments, or renewable energy credits. These incentives can reduce your upfront costs by 40-50% or more, significantly accelerating your return on investment.
Property Value Enhancement
Multiple studies have demonstrated that homes with solar installations sell for more than comparable homes without them. Research suggests that solar panels can increase home values by approximately 4%, though this varies by location. Buyers increasingly view solar as a desirable feature, recognising both the energy savings and environmental benefits.
Energy Independence and Price Protection
Solar panels provide a hedge against rising electricity costs. While utility rates have consistently increased over time, your solar system’s production costs remain fixed after installation. This price certainty becomes increasingly valuable over decades of ownership. Additionally, with battery storage, you gain protection against power outages and greater energy independence.
Environmental Considerations
Beyond finances, solar delivers substantial environmental benefits. The average residential solar system offsets approximately 100 tons of carbon dioxide over its lifetime, equivalent to planting 2,500 trees. For environmentally conscious homeowners, this impact represents value that transcends monetary calculations.
Factors That Affect Solar’s Value
Several variables influence whether solar makes sense for your situation. Sunlight exposure is critical in homes in sunny climates with minimal shading, resulting in better returns. Your current electricity rates matter significantly; higher rates mean greater savings potential. Roof condition and orientation affect both installation costs and system performance. Finally, available incentives vary dramatically by location, making solar far more attractive in some areas than others.
The verdict? For most homeowners with suitable conditions, adequate sunlight, decent roof space, and reasonable electricity costs, solar represents a solid investment with both financial and environmental returns.

How to Install a Solar Panel at Home
Installing solar panels is a complex project that typically requires professional assistance, but understanding the process helps you make informed decisions and manage the project effectively.
Step 1: Assess Your Home’s Solar Potential
Begin by evaluating whether your home is suitable for solar. Examine your roof’s orientation. South-facing roofs work best in the Northern Hemisphere, though east and west orientations can also be productive. Check for shading from trees, buildings, or chimneys that might block sunlight during peak hours. Assess your roof’s condition; if it needs replacement soon, do that before installing panels. Finally, review your electricity bills to understand your consumption patterns and determine appropriate system sizing.
Step 2: Research and Get Multiple Quotes
Don’t rush into solar. Research local installers, read reviews, and request quotes from at least three reputable companies. Compare not just prices but also equipment quality, warranties, and company track records. Ask about the specific panels and inverters they recommend, financing options, and projected energy production. Be wary of high-pressure sales tactics. For homeowners in Australia, companies like Reds Power Solutions in Sydney offer professional solar installation services with expertise in local conditions and regulations.
Step 3: Understand Financing Options
You have several paths to solar ownership. Purchasing outright provides the best long-term returns and full access to incentives. Solar loans allow you to own the system while spreading payments over time. Alternatively, solar leases or power purchase agreements (PPAs) require no upfront investment but offer smaller savings since you don’t own the system.
Step 4: Navigate Permits and Approvals
Professional installers typically handle permitting, but you should know the process. You’ll need building permits from your local government and potentially approval from your homeowners’ association. You’ll also need approval from your utility company for grid connection and net metering, which allows you to sell excess power back to the grid.
Step 5: The Installation Process
Once approved, installation typically takes one to three days. The crew will install mounting hardware on your roof, securing it to rafters for stability. They’ll carefully position and attach the solar panels, then run electrical wiring from the panels to the inverter and from the inverter to your electrical panel. Finally, they’ll install the inverter and any monitoring equipment.
Step 6: Inspection and Grid Connection
After installation, a local building inspector will verify that everything meets code requirements. Your utility company will then inspect and approve the grid connection. Once you receive final approval, your system can be activated and begin producing electricity.
Step 7: Monitoring and Maintenance
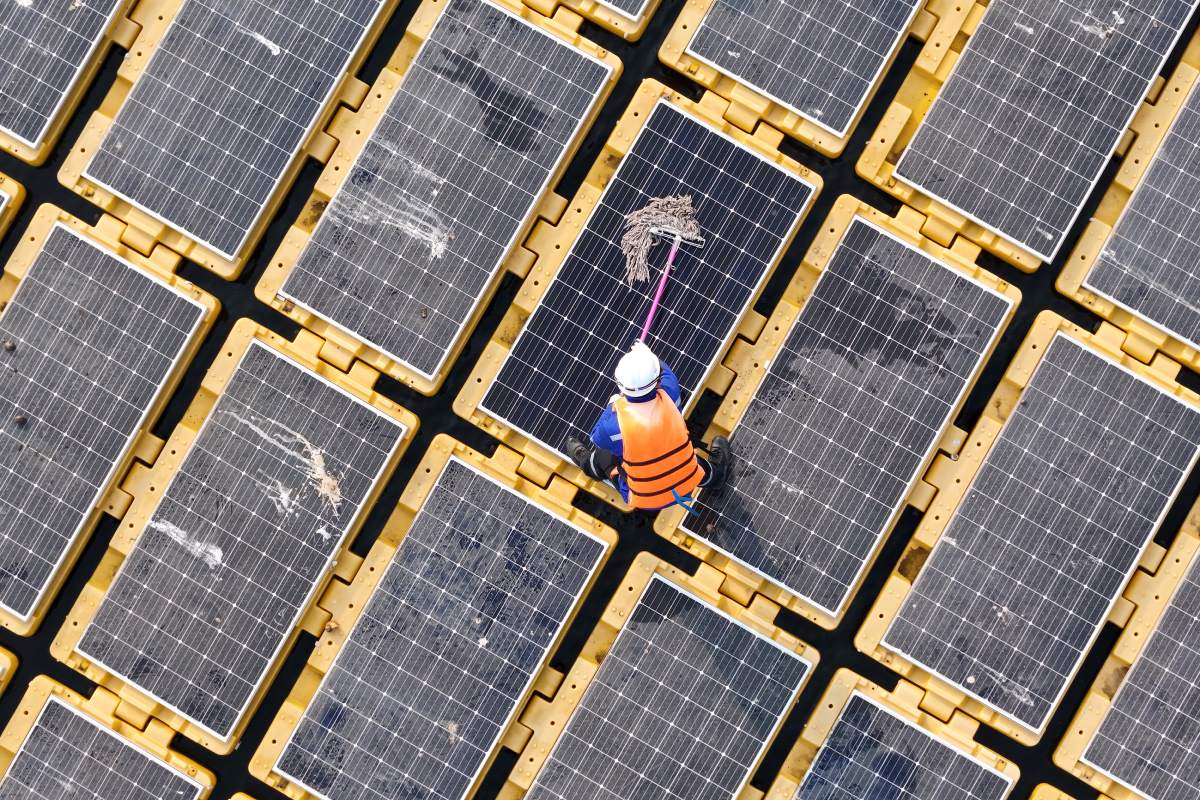
Solar panels require minimal maintenance but benefit from occasional attention. Monitor your system’s performance through the provided app or website, watching for any production anomalies. Clean panels annually or when visibly dirty, though rain often handles this naturally. Have a professional inspection every few years to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
Solar panels represent a mature, reliable technology that offers compelling benefits for many homeowners. While they require a significant initial investment, the combination of energy savings, incentives, property value increases, and environmental impact makes solar an attractive option for those with suitable conditions. As technology improves and costs continue declining, solar energy will likely become an even more obvious choice for homeowners seeking energy independence and sustainability.
Whether you’re motivated by financial returns, environmental consciousness, or energy security, understanding solar panels and their installation process empowers you to make confident decisions about your home’s energy future.